Now days we are getting our computer equipped with more and more power even now we are getting quad core processor is also at lower price. Since we have multicore processors are now so we can take advantages of multicore processor with parallel execution in C# 4.0. There are some time consuming task for the computer for example a long for loop or similar kind of things. This kind of task can be done parallel with parallel class in C# 4.0.
Now in C# 4.0 you have the Parallel static class with the help of this you can perform task parallel very easily. In this post I am going to explain Parallel for loop. Let’s take a very simple example. First lets create a example with simple for loop. Following is code for that.
In the above its a normal loop which increments I and then print the that number into the console screen and Here is the output.

Here in the output you can see its sequentially process one by one now lets change this code to parallel for loop like following.
Here in the above code you can see that I have used parallel for which also prints the Incremented integer in console application. Now let’s run that code and see the output as following.
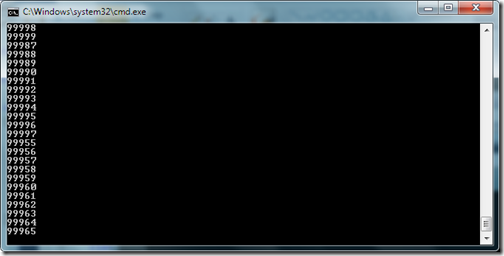
If you see the output very carefully then you can see that its not processing sequentially one by one but its processing it parallel and its will be much faster if you have multicore processor in your computer. But beware if you are going to run in simple processor computer its going to take more time then normal computer. That’s it. Hope you liked it.. Stay tuned for more.. Till that happy programming..
Now in C# 4.0 you have the Parallel static class with the help of this you can perform task parallel very easily. In this post I am going to explain Parallel for loop. Let’s take a very simple example. First lets create a example with simple for loop. Following is code for that.
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
using System.Text;
using System.Threading.Tasks;
using System.Diagnostics;
namespace Parallel
{
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
for (int i = 0; i <=100000; i++)
{
Console.WriteLine(i);
}
}
}
}
In the above its a normal loop which increments I and then print the that number into the console screen and Here is the output.

Here in the output you can see its sequentially process one by one now lets change this code to parallel for loop like following.
using System;
namespace Parallel
{
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
System.Threading.Tasks.Parallel.For(0, 100000, i =>
{
Console.WriteLine(i);
}
);
Console.ReadLine();
}
}
}
Here in the above code you can see that I have used parallel for which also prints the Incremented integer in console application. Now let’s run that code and see the output as following.

If you see the output very carefully then you can see that its not processing sequentially one by one but its processing it parallel and its will be much faster if you have multicore processor in your computer. But beware if you are going to run in simple processor computer its going to take more time then normal computer. That’s it. Hope you liked it.. Stay tuned for more.. Till that happy programming..